What Is Cv and Why It Matters
Cv (flow coefficient) is a standardized measure of a valve’s capacity to pass fluid. It represents the number of U.S. gallons per minute (gpm) of water at 60 °F that will flow through a valve with a 1 psi pressure drop. In practice, Cv allows engineers to compare valve sizes, ensure proper flow, and avoid pressure loss or instability.
Why Cv Matters
- Valve Sizing & Selection – Correct Cv ensures adequate flow without oversizing or undersizing the valve.
- Energy Efficiency – Matching Cv minimizes pressure loss, reducing pump energy and operating costs.
- Process Stability – Proper Cv improves control response and prevents oscillations.
Standard Reference Conditions
Because fluid properties (density, viscosity) vary with temperature, Cv is always referenced to a standard temperature for consistent comparison:
- Liquid Cv: Defined using water at 60 °F for consistent comparison.
- Kvs (Metric Standard): Flow in m³/h of water at 5–30 °C with a 1 bar drop.
– Conversion: Kvs ≈ 0.865 × Cv.
For fluids with vastly different temperatures or viscosities, corrections are required.
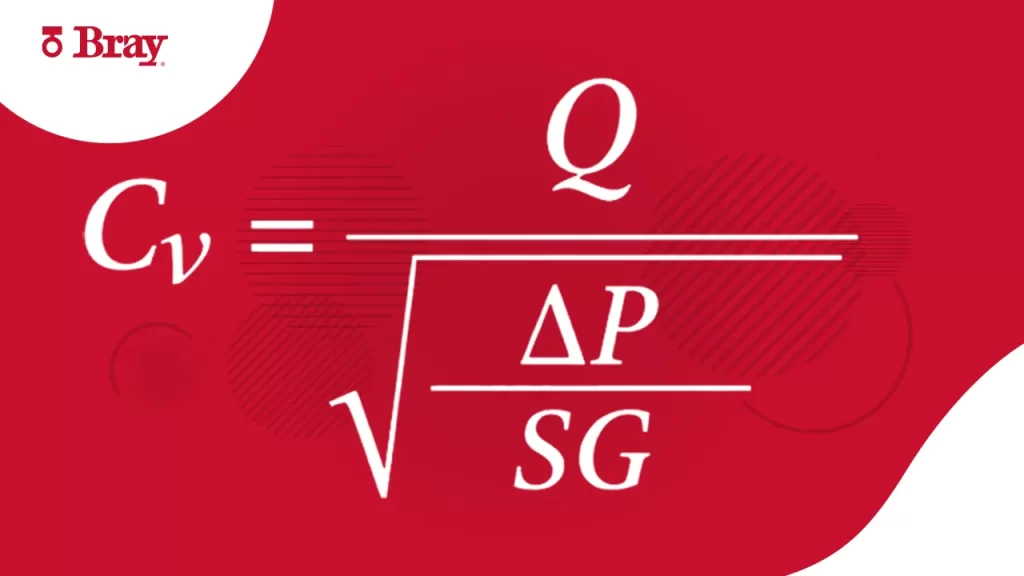
Cv Formula
For liquid service:
Cv = Q × √ (SG/ΔP)
Where:
- Q = Flow (gpm)
- ΔP = Pressure drop across the valve (1-5 psi common)
- SG = Fluid specific gravity (Water is 1)
- This is the formula: Cv = Q x √ (SG/ΔP)
Step-by-Step Example
- Flow = 150 gpm
- ΔP = 5 psi
- SG = 0.85 (glycol in this example) (Water would be 1)
- √ (5/0.85) = 2.426
- Cv = 150 / 2.426 ≈ 8
- Select a valve with Cv ≥ 62.
- Always confirm with the valve manufacturer’s Cv curves.
- Water Example: 100 gpm, ΔP = 4 psi, SG = 1 → Cv = 50.
Practical Considerations
- Temperature: Viscosity shifts at high/low temperatures can affect performance.
- Rangeability: Valve must modulate effectively across load changes.
- Safety Margins: Consider future flow increases or temperature swings.
- Special Fluids: Slurries or oils may need non-standard sizing.
Conclusion
Cv provides a reliable, standardized way to size and compare valves. Using the correct Cv ensures efficient, stable, and cost-effective system control while avoiding energy waste and operational issues.
Valve Sizing Calculator
Bray Commercial Division offers a free Valve Sizing Calculator accessible at https://www.braycommercialdivision.com/ecom designed to streamline Cv-based valve selection. You’ll find the calculator widget in the top left corner of the page immediately upon loading. It provides a guided interface to calculate required Cv values and recommend both Pressure Independent Control Valves (PICV) and Pressure Dependent Control Valves (PDCV) for your application.
Supported Valve Types
- Pressure Independent Control Valves (PICV)
Function: Automatically maintain a constant flow rate regardless of inlet pressure fluctuations.
Sizing Implication: PICVs combine a control valve, differential pressure regulator, and balancing device in one body so the calculator factors in the built-in regulator’s rangeability when determining Cv requirements.
- Pressure Dependent Control Valves (PDCV)
Function: Flow varies directly with upstream differential pressure.
Sizing Implication: PDCV sizing relies solely on the Cv equation at the operating ΔP point. The calculator uses your specified maximum ΔP to compute the required Cv and suggests valves who’s published Cv at that ΔP meet or exceed your needs.
How to Use the Valve Sizing Calculator
- Navigate to the Calculator
- Go to https://www.braycommercialdivision.com/ecom and locate the sizing tool in the top-left of the interface.
- Select Valve Category
- Pressure Independent (default) or
- Pressure Dependent
- Input Process Parameters
- Flow Rate (Q): Enter the desired volumetric flow (gpm or m³/h).
- Pressure Drop (ΔP): Specify the maximum allowable differential pressure (psi or bar).
- Fluid Properties: Choose water (standard at 60 °F/15 °C) or enter specific gravity for other fluids.
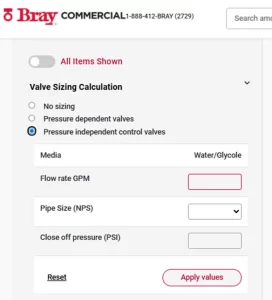
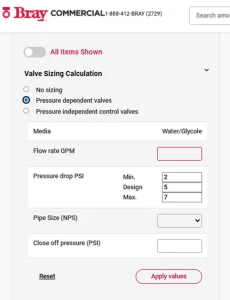
View Calculated Cv
The calculator instantly computes the required Cv (or Kvs) using the standard liquid formula and displays the numeric result. (See above)
Review Valve Recommendations
Based on your inputs, the tool suggests Bray valve models with published Cv curves that match or exceed the calculated requirement at your operating conditions.
Export & Share
You can download a PDF summary of your inputs, Cv results, and recommended valve part numbers—ideal for specifying in technical submittals or procurement documents.
Benefits of the Online Calculator
- Speed & Accuracy: Automates manual Cv calculations and sizing checks, reducing human error.
- Built-In Corrections: Applies proper conversions between Cv and international Kvs units.
- Valve-Specific Data: Links directly to Bray model curves—no need to hunt through catalogs.
- Documentation Ready: Generates exportable reports for engineering reviews and P.O. generation.
Integrating Calculator Use with Manual Cv Workflows
While manual Cv calculations (as described earlier) remain fundamental for understanding fluid dynamics, the online calculator:
Validates Your Hand Calculations
Cross-check your hand-derived Cv with the tool’s result.
Explores “What-If” Scenarios
Quickly adjust flow, ΔP, or fluid SG to see real-time effects on required Cv.
Compares Valve Types
- Toggle between PIV and PDCV modes to understand trade-offs—especially useful when deciding between energy-efficient pressure-independent solutions or simpler pressure-dependent valves.
- By leveraging Bray’s free Valve Sizing Calculator alongside traditional Cv formulas, engineers can expedite valve selection, ensure optimal system performance, and confidently specify the correct valve technology for any HVAC, hydronic, or process-control application.